What Are Whole Foods?
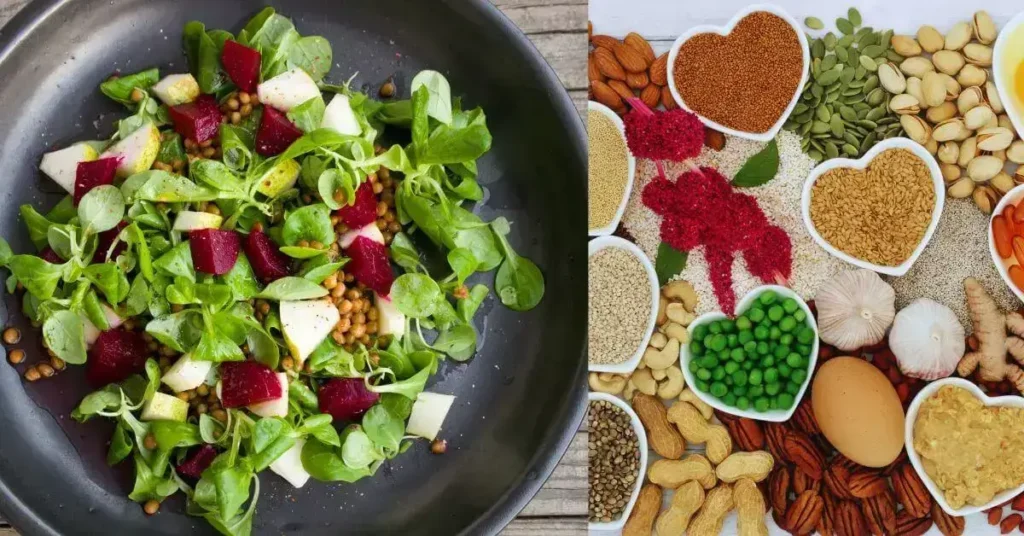
What Are Whole Foods? In a world filled with convenience and processed options, “whole foods” has become a beacon of health and nutrition. Whole foods are unprocessed and unrefined, maintaining their natural state and nutritional value. Embracing these foods can transform your well-being, offering many benefits beyond just the healthy aspect.
Definition of Whole Foods
Types of Whole Foods
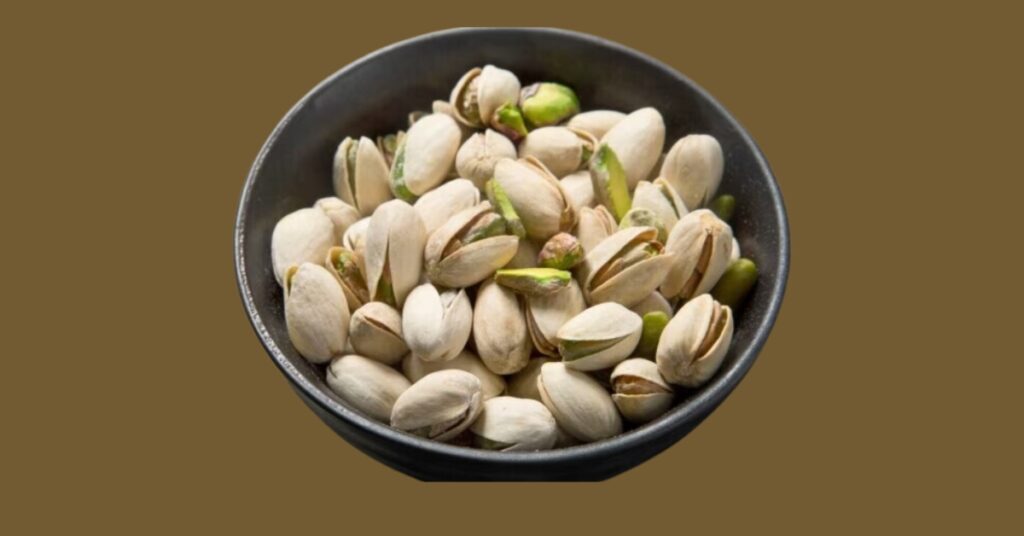
Whole foods encompass a variety of categories, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are not altered or stripped of their essential components, providing a holistic approach to nutrition.
Nutritional Benefits
Rich in Essential Nutrients
Whole foods are a powerhouse of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Unlike processed alternatives, they offer a complete nutritional package, promoting overall health and vitality.
High Fiber Content
The high fiber content in whole foods contributes to improved digestion, weight management, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases. Fiber not only aids in maintaining a healthy digestive system but also keeps you feeling full and satisfied.
Nutrient Absorption and Bioavailability
The synergy of nutrients in whole foods enhances their absorption and bioavailability, ensuring that your body can make the most of the nutritional goodness present in these foods.
Examples of Whole Foods
Fruits and Vegetables
The vibrant colors of fruits and vegetables signify a rich array of nutrients. From the antioxidants in berries to the vitamins in leafy greens, incorporating a rainbow of produce ensures a diverse nutritional intake.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats are packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Choosing whole grains over refined options provides sustained energy and promotes cardiovascular health.
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and legumes are essential for muscle development, immune function, and overall cellular health. They offer a nutrient-dense alternative to processed protein sources.
Healthy Fats
Avocados, nuts, and olive oil are excellent sources of healthy fats. These fats play a crucial role in brain health, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Impact on Health
Weight Management
The nutrient density and fiber in whole foods contribute to a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management. Unlike empty-calorie processed foods, whole foods provide sustained energy without unnecessary additives.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Studies show that a diet rich in whole foods reduces the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. The natural compounds in these foods act as protective agents for your overall health.
Improved Digestion
The fiber and enzymes in whole foods support a healthy digestive system, reducing the risk of constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. A well-functioning digestive system is fundamental to overall well-being.
Whole Foods vs. Processed Foods
Nutrient Comparison
Comparing the nutrient profiles of whole and processed foods reveals a stark difference. Whole foods are nutrient-dense, providing a broad spectrum of essential elements, while processed foods often lack vital nutrients due to refining and manufacturing processes.
Impact on Overall Health
The long-term impact of a diet predominantly consisting of processed foods can lead to various health issues, including obesity, cardiovascular problems, and metabolic disorders. Making informed choices about the foods you consume is crucial for sustained well-being.
Making Informed Choices
Understanding food labels and ingredients empowers you to make informed choices. Opting for whole, minimally processed foods over heavily processed alternatives is a step towards prioritizing your health.
Incorporating Whole Foods into Your Diet
Practical Tips for Meal Planning
Embarking on a journey toward a whole-food diet may seem daunting, but practical meal-planning tips make it a feasible and enjoyable process. Planning your meals allows you to incorporate whole foods into your daily routine.
Simple Whole Food Recipes
Simple recipes can make whole foods a delicious part of your diet, from vibrant salads to hearty grain bowls. Experimenting with flavors and textures ensures you find joy in nourishing your body.
Gradual Transition for Beginners
A gradual transition can be more sustainable for those new to whole foods. Start by incorporating one or two entire food meals a day and gradually increase as your taste buds adjust to the richness of natural flavors.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in Adopting a Whole Food Diet
Challenges such as time constraints, perceived high costs, and unfamiliarity with certain foods can hinder the adoption of a whole-food diet. Acknowledging these challenges is the first step towards overcoming them.
Strategies for Overcoming Barriers
Simple strategies, such as meal prepping, budget-friendly shopping, and gradually introducing new foods, can help overcome common barriers. Education and awareness play critical roles in dismantling misconceptions about the accessibility and affordability of whole foods.
Whole Foods for Different Lifestyles
Whole Foods for Vegetarians and Vegans
Vegetarians and vegans can embrace whole foods through plant-based options like legumes, nuts, seeds, and fruits and vegetables. Ensuring a diverse intake covers essential nutrients typically found in animal products.
Whole Foods for Athletes
Athletes benefit from the sustained energy provided by whole foods. A combination of complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports endurance, muscle recovery, and overall athletic performance.
Whole Foods for Busy Professionals
Even with a hectic schedule, busy professionals can prioritize whole foods by opting for quick and nutritious options. Preparing simple meals in advance and having wholesome snacks on hand can make a significant difference in maintaining energy levels throughout the day.
Economic Considerations
Dispelling the Myth of Whole Foods Being Expensive
While there is a common misconception that whole foods are expensive, strategic shopping, bulk purchasing, and seasonality can make an entire diet cost-effective. Investing in your health now may lead to long-term savings on healthcare costs.
Long-Term Savings on Healthcare Costs
The preventive nature of a whole-food diet can contribute to long-term savings on healthcare expenses. By reducing the risk of chronic diseases, you are investing in your well-being and potentially avoiding costly medical treatments.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability of Whole Food Choices
Choosing whole foods also has positive implications for the environment. By supporting sustainable farming practices and reducing reliance on heavily processed foods, you contribute to a healthier planet.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
The production and transportation of heavily processed foods often contribute to a significant carbon footprint. Opting for locally sourced, whole foods minimizes the environmental impact associated with food consumption.
FAQs: What Are Whole Foods?
What Defines a Food as “Whole”?
Whole foods are naturally unprocessed free from additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients. Examples include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Can I Still Enjoy Treats While Following a Whole Food Diet?
Yes, indulging in treats occasionally is acceptable. The key is moderation. Choose whole food-based treats or prepare homemade versions to maintain the integrity of your diet.
How Can I Afford a Whole Food Diet on a Budget?
Strategic shopping, buying in bulk, and focusing on seasonal produce can make a whole-food diet budget-friendly. Planning meals and minimizing food waste also contribute to cost-effectiveness.
Are There Any Specific Whole Food for Weight Loss?
Whole foods rich in fiber and low in processed sugars can support weight loss. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your diet for a balanced approach to weight management.
How Do I Start Incorporating Foods into My Diet?
Start with minor changes. Gradually replace processed foods with whole alternatives. Experiment with new recipes and flavors to discover the joy of nourishing your body with wholesome, natural foods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embracing a whole-food lifestyle goes beyond a trend; it’s a commitment to your and the planet’s health. By understanding the definition, benefits, and practical aspects of whole foods, you can make informed choices that resonate with your unique lifestyle. So, take the first step on this flavorful journey, savoring the richness of whole foods and reaping the rewards of a well-nourished life.